-
JUNGOL/Intermediate_Coder/그래프탐색-DFS/2462 : 키 순서코딩 테스트/JUNGOL 2022. 1. 20. 16:51
Intermediate_Coder/그래프탐색-DFS/키 순서
문제
1번부터 N번까지 번호가 붙여져 있는 학생들에 대하여 두 학생끼리 키를 비교한 결과의 일부가 주어져 있다.
단, N명의 학생들의 키는 모두 다르다고 가정한다.
예를 들어, 6명의 학생들에 대하여 6번만 키를 비교하였고, 그 결과가 다음과 같다고 하자.
1번 학생의 키 < 5번 학생의 키
3번 학생의 키 < 4번 학생의 키
5번 학생의 키 < 4번 학생의 키
4번 학생의 키 < 2번 학생의 키
4번 학생의 키 < 6번 학생의 키
5번 학생의 키 < 2번 학생의 키
이 비교 결과로부터 모든 학생 중에서 키가 가장 작은 학생부터 자신이 몇 번째인지 알 수 있는 학생들도 있고
그렇지 못한 학생들도 있다는 사실을 아래처럼 그림을 그려 쉽게 확인할 수 있다.
a번 학생의 키가 b번 학생의 키보다 작다면, a에서 b로 화살표를 그려서 표현하였다.
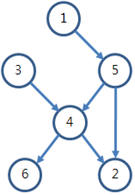
JUNGOL 키 순서 1번은 5번보다 키가 작고, 5번은 4번보다 작기 때문에, 1번은 4번보다 작게 된다.
그러면 1번, 3번, 5번은 모두 4번보다 작게 된다.
또한 4번은 2번과 6번보다 작기 때문에, 4번 학생은 자기보다 작은 학생이 3명이 있고,
자기보다 큰 학생이 2명이 있게 되어 자신의 키가 몇 번째인지 정확히 알 수 있다.
그러나 4번을 제외한 학생들은 자신의 키가 몇 번째인지 알 수 없다.
학생들의 키를 비교한 결과가 주어질 때,
자신의 키가 몇 번째인지 알 수 있는 학생들이 모두 몇 명인지 계산하여 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력 형식
입력 파일의 첫째 줄에 학생들의 수 N(2≤N≤500)과 학생 키를 비교한 횟수 M(0≤M≤N(N-1)/2)이 주어진다.
다음 M개의 각 줄에는 두 학생의 키를 비교한 결과를 나타내는 두 양의 정수 a와 b가 주어진다.
이는 번호가 a인 학생이 번호가 b인 학생보다 키가 작은 것을 의미한다.
출력 형식
자신의 키가 몇 번째인지 알 수 있는 학생이 모두 몇 명인지를 출력한다.
[제약조건]
• 전체 테스트 데이터의 50%는 N≤200
• 전체 테스트 데이터의 80%는 N≤350
입력 예
6 6 | 6 7 | 6 3
1 5 | 1 3 | 1 2
3 4 | 1 5 | 2 3
5 4 | 3 4 | 4 5
4 2 | 5 4
4 6 | 4 2
5 2 | 4 6| 5 2
출력 예
1 | 2 | 0
OrderByHeight.h
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <stack> using std::vector; using std::stack; class OrderByHeight : public Base { private: struct Student { Student() : knownCount(0), isChecked(false) {} vector<int> forwards; int knownCount; bool isChecked; }; int GetKnownStudentCount(vector<Student>& students, int n); void ResetCheckedStudents(vector<Student>& students, int n); };OrderByHeight.cpp
void OrderByHeight::Code() { int n, m; std::cin >> n >> m; vector<Student> students(n + 1, Student()); for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int behind, forward; std::cin >> behind >> forward; students[behind].forwards.push_back(forward); } std::cout << GetKnownStudentCount(students, n); } /// <summary> /// 자신의 키를 알고 있는 학생의 수를 반환한다. /// </summary> /// <param name="students">학생 정보 리스트</param> /// <param name="n">학생의 수</param> /// <returns>자신의 키를 아는 학생의 수</returns> int OrderByHeight::GetKnownStudentCount(vector<Student>& students, int n) { int knownStudentCount{ 0 }; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (students[i].forwards.empty()) { continue; } stack<int> s; s.push(i); while (!s.empty()) { int curStudent{ s.top() }; s.pop(); for (int nextStudent : students[curStudent].forwards) { if (!students[nextStudent].isChecked) { students[i].knownCount++; students[nextStudent].knownCount++; students[nextStudent].isChecked = true; s.push(nextStudent); } } } ResetCheckedStudents(students, n); } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (students[i].knownCount == n - 1) { knownStudentCount++; } } return knownStudentCount; } /// <summary> /// 각 학생의 확인 여부를 초기화한다. /// </summary> /// <param name="students">학생 정보 리스트</param> /// <param name="n">학생의 수</param> void OrderByHeight::ResetCheckedStudents(vector<Student>& students, int n) { for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { students[i].isChecked = false; } }
실행 결과 Success(100)
코드 해설
각 학생은 자신의 앞에 있는 학생은 알 수 있으므로 자신의 앞에 있는 학생을 순회하며 자신이 뒤에 있는 것을 알리고 알 고 있는 순서의 개수를 추가하고 자신이 알고 있는 순서의 개수도 추가해 주는 것을 모든 학생에 대해 실행하면 각각의 학생은 자신의 앞, 뒤의 학생 수를 알 수 있게 된다.
이를 전체 학생 수와 비교하면 자신의 키 순서를 아는 학생의 수를 알 수 있게 된다.
stack<int> s; s.push(i); while (!s.empty()) { int curStudent{ s.top() }; s.pop(); for (int nextStudent : students[curStudent].forwards) { if (!students[nextStudent].isChecked) { students[i].knownCount++; students[nextStudent].knownCount++; students[nextStudent].isChecked = true; s.push(nextStudent); } } }이때, 다른 학생이 가리키는 학생을 중복해서 체크하는 것을 막기 위해 플래그를 추가하여 검사하도록 한다.
if (!students[nextStudent].isChecked)NadanKim/CodingTest_JUNGOL: JUNGOL 코딩 테스트를 위한 저장소 (github.com)
NadanKim/CodingTest_JUNGOL
JUNGOL 코딩 테스트를 위한 저장소. Contribute to NadanKim/CodingTest_JUNGOL development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com