-
JUNGOL/Intermediate_Coder/그래프탐색-DFS/1695 : 단지번호붙이기코딩 테스트/JUNGOL 2021. 12. 10. 19:16
Intermediate_Coder/그래프탐색-DFS/단지번호붙이기
문제
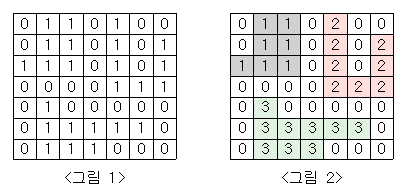
<그림 1>과 같이 정사각형 모양의 지도가 있다. 1은 집이 있는 곳을, 0은 집이 없는 곳을 나타낸다.
철수는 이 지도를 가지고 연결된 집들의 모임인 단지를 정의하고, 단지에 번호를 붙이려 한다. 여기서 연결되었다는 것은 어떤 집이 좌우, 혹은 아래위로 다른 집이 있는 경우를 말한다. 대각선상에 집이 있는 경우는 연결된 것이 아니다. <그림 2>는 <그림 1>을 단지별로 번호를 붙인 것이다.
지도를 입력하여 단지수를 출력하고, 각 단지에 속하는 집의 수를 오름차순으로 정렬하여 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
JUNGOL 그래프탐색-DFS 단지번호붙이기 입력 형식
첫 번째 줄에는 지도의 크기 N(정사각형임으로 가로와 세로의 크기는 같으며 5≤N≤25)이 입력되고, 그 다음 N줄에는 각각 N개의 자료(0혹은 1)가 입력된다.
출력 형식
첫 번째 줄에는 총 단지수를 출력하시오. 그리고 각 단지내 집의 수를 오름차순으로 정렬하여 한 줄에 하나씩 출력하시오.
입력 예
7
0110100
0110101
1110101
0000111
0100000
0111110
0111000출력 예
3
7
8
9
NumberingHouse.h
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <map> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> using std::string; using std::map; using std::vector; using std::queue; class NumberingHouse : public Base { private: struct Point { Point(int x, int y) :x(x), y(y) {} int x, y; }; int Numbering(int** arr, int n, map<int, int>& result); void Counting(int** arr, int n, int x, int y, int number, map<int, int>& result); };NumberingHouse.cpp
void NumberingHouse::Code() { int n; std::cin >> n; int** arr = new int*[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { arr[i] = new int[n]; string temp; std::cin >> temp; for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) { int tempValue = temp[j] - '0'; arr[i][j] = tempValue % 10; } } map<int, int> resultMap; int number{ Numbering(arr, n, resultMap) }; vector<int> resultList; for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) { resultList.push_back(resultMap[i]); } std::sort(resultList.begin(), resultList.end()); std::cout << number << '\n'; for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) { std::cout << resultList[i] << '\n'; } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { delete[] arr[i]; } delete[] arr; } /// <summary> /// 주어진 집에 단지 번호를 붙이고 단지마다의 개수를 카운트한다. /// </summary> /// <param name="arr">건물 배열</param> /// <param name="n">배열의 길이</param> /// <param name="result">단지 번호 붙인 결과</param> /// <returns>단지의 개수</returns> int NumberingHouse::Numbering(int** arr, int n, map<int, int>& result) { int number{ 0 }; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (arr[i][j] != 0) { number++; Counting(arr, n, j, i, number, result); } } } return number; } /// <summary> /// 주어진 좌표를 기준으로 단지 번호를 붙이면서 개수를 센다. /// </summary> /// <param name="arr">건물 배열</param> /// <param name="n">배열의 길이</param> /// <param name="x">시작 x 좌표</param> /// <param name="y">시작 y 좌표</param> /// <param name="number">단지 번호</param> /// <param name="result">단지 번호 붙인 결과</param> void NumberingHouse::Counting(int** arr, int n, int x, int y, int number, map<int, int>& result) { result[number] = 1; arr[y][x] = 0; queue<Point> q; q.push(Point(x, y)); while (!q.empty()) { Point curPos = q.front(); q.pop(); int oldX{ curPos.x }, oldY{ curPos.y }; for (int i = -1; i <= 1; i += 2) { int newX{ oldX + i }, newY{ oldY + i }; if (0 <= newX && newX < n) { if (arr[oldY][newX] != 0) { result[number]++; arr[oldY][newX] = 0; q.push(Point(newX, oldY)); } } if (0 <= newY && newY < n) { if (arr[newY][oldX] != 0) { result[number]++; arr[newY][oldX] = 0; q.push(Point(oldX, newY)); } } } } }
실행 결과 Success(100)
코드해설
연속된 부분을 찾아 개수를 구하면 되는 문제로 시작 지점에서 상하좌우를 확인하여 이동 가능한 경우 해당 부분을 체크하는 방식으로 진행하면 된다. 나는 큐를 사용하여 BFS로 풀었지만 스택을 사용하면 DFS로 풀이하는 게 된다.
각 단지의 시작 부분을 배열의 좌상단에서부터 순서대로 찾다가 건물이 있는 부분을 발견하면 연결된 건물을 찾는 함수를 실행한다.
int NumberingHouse::Numbering(int** arr, int n, map<int, int>& result) { int number{ 0 }; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (arr[i][j] != 0) { number++; Counting(arr, n, j, i, number, result); } } } return number; }최초 진입 시 단지 번호에 따라 개수를 구하기 위해 입력된 위치를 체크하고, 단지의 개수를 설정해준다.
result[number] = 1; arr[y][x] = 0;이동 가능하고 건물이 있는 부분을 체크하고 해당 부분에서 다시 검색하기 위해 큐에 값을 넣어준다.
if (0 <= newX && newX < n) { if (arr[oldY][newX] != 0) { result[number]++; arr[oldY][newX] = 0; q.push(Point(newX, oldY)); } }NadanKim/CodingTest_JUNGOL: JUNGOL 코딩 테스트를 위한 저장소 (github.com)
NadanKim/CodingTest_JUNGOL
JUNGOL 코딩 테스트를 위한 저장소. Contribute to NadanKim/CodingTest_JUNGOL development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com