-
JUNGOL 기초다지기 12 함수2보관함 2019. 12. 11. 21:19
프로그래밍에서 가장 기초적인 내용을 다루는 기초 다지기입니다.
이번 포스팅은 기초 다지기 중 열두 번째인 함수2 문제를 풀어보도록 하겠습니다.
기초 내용인 만큼 다른 설명없이 문제와 코드만 간단하게 작성하도록 하겠습니다.
579 : 함수2 - 자가진단1

#include <iostream> using namespace std; void PrintDesc(int arr[], int n); void Swap(int& a, int& b); int main(void) { int* arr = nullptr; int n; cin >> n; arr = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { cin >> arr[i]; } PrintDesc(arr, n); delete[] arr; } void PrintDesc(int arr[], int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int max = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) { if (arr[max] < arr[j]) max = j; } Swap(arr[i], arr[max]); cout << arr[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; } void Swap(int& a, int& b) { int temp = a; a = b; b = temp; }580 : 함수2 - 자가진단2

#include <iostream> using namespace std; bool IsValidDate(int m, int d); int main(void) { int m, d; cin >> m >> d; if (IsValidDate(m, d)) cout << "OK!" << endl; else cout << "BAD!" << endl; } bool IsValidDate(int m, int d) { static int arr[13]{ 0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 }; if (m > 12) return false; if (m < 1) return false; if (d > arr[m]) return false; if (d < 1) return false; return true; }581 : 함수2 - 자가진단3

이번 문제는 특정 자료형으로 함수를 만들어야 하는데 연습삼아 템플릿을 사용해 봤습니다.
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template <typename T> void PrintBig(T a, T b); template <typename T> void PrintSmall(T a, T b); template <typename T> T GetAbsolute(T num); int main(void) { int var1, var2; cin >> var1 >> var2; cout.setf(ios::fixed); cout.precision(2); PrintBig(var1, var2); float var3, var4; cin >> var3 >> var4; PrintSmall(var3, var4); } template <typename T> void PrintBig(T a, T b) { T big = (GetAbsolute(a) > GetAbsolute(b)) ? a : b; cout << big << endl; } template <typename T> void PrintSmall(T a, T b) { T small = (GetAbsolute(a) < GetAbsolute(b)) ? a : b; cout << small << endl; } template <typename T> T GetAbsolute(T num) { if (num > 0) return num; else return -num; }582 : 함수2 - 자가진단4

이번에는 루트값을 구해야하기 때문에 cmath를 인클루드하여 사용하였습니다.
#include <iostream> #include <cmath> using namespace std; void PrintRadius(float size); int main(void) { float var; cin >> var; cout.setf(ios::fixed); cout.precision(2); PrintRadius(var); } void PrintRadius(float size) { float radius = sqrt(size / 3.14); cout << radius << endl; }583 : 함수2 - 자가진단5

#include <iostream> #include <cmath> using namespace std; void PrintSpecificValue(float a, float b, float c); float GetBig(float a, float b); float GetSmall(float a, float b); float GetMid(float a, float b, float c); int main(void) { float var1, var2, var3; cin >> var1 >> var2 >> var3; PrintSpecificValue(var1, var2, var3); } void PrintSpecificValue(float a, float b, float c) { int big = ceil(GetBig(GetBig(a, b), c)); int small = floor(GetSmall(GetSmall(a, b), c)); int rest = floor(GetMid(a, b, c) + 0.5f); cout << big << ' ' << small << ' ' << rest << endl; } float GetBig(float a, float b) { if (a > b) return a; else return b; } float GetSmall(float a, float b) { if (a < b) return a; else return b; } float GetMid(float a, float b, float c) { float big = GetBig(GetBig(a, b), c); float small = GetSmall(GetSmall(a, b), c); if (a != big && a != small) return a; if (b != big && b != small) return b; if (c != big && c != small) return c; }584 : 함수2 - 자가진단6

#include <iostream> using namespace std; void PrintAll123(); int main(void) { PrintAll123(); } void PrintAll123() { for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i) { for (int j = 1; j <= 3; ++j) { cout << i << " + " << j << " = " << i + j << endl; } } }585 : 함수2 - 자가진단7
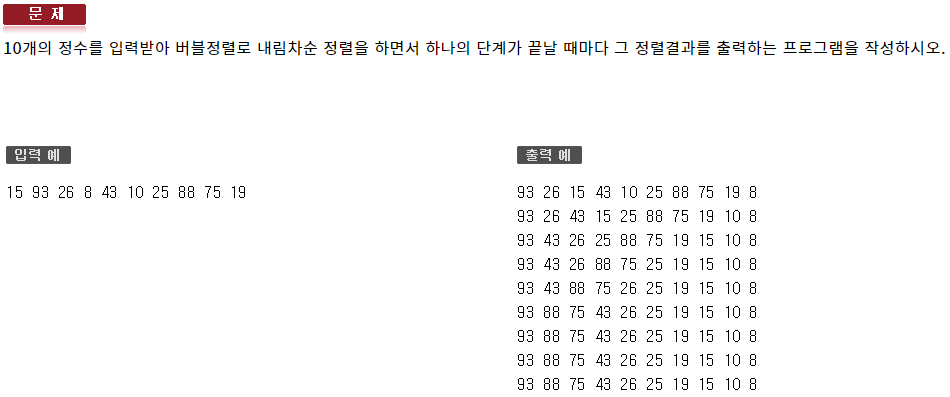
#include <iostream> using namespace std; void PrintBubbleSort(int arr[]); void Swap(int& a, int& b); void PrintArr(int arr[]); int main(void) { int arr[10]; for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { cin >> arr[i]; } PrintBubbleSort(arr); } void PrintBubbleSort(int arr[]) { for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < 9 - i; ++j) { if (arr[j] < arr[j + 1]) Swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]); } PrintArr(arr); } } void Swap(int& a, int& b) { int temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } void PrintArr(int arr[]) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { cout << arr[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; }586 : 함수2 - 자가진단8

오랜만에 매크로 함수가 나왔습니다. 여기에서 함정이 발생하는데 pow2(var1 - var2)로 작성하면 var1 - var2 * var1 - var2가 되어 예상과는 다른 답이 나옵니다.
#include <iostream> #define pow2(a) a * a #define pow3(a) a * a * a using namespace std; int main(void) { int var1, var2; cin >> var1 >> var2; cout << "(" << var1 << " - " << var2 << ") ^ 2 = " << pow2((var1 - var2)) << endl; cout << "(" << var1 << " + " << var2 << ") ^ 3 = " << pow3((var1 + var2)) << endl; }175 : 함수2 - 형성평가1

#include <iostream> using namespace std; void PrintDesc(int arr[], int n); int main(void) { int n; cin >> n; int* arr = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { cin >> arr[i]; } PrintDesc(arr, n); delete[] arr; } void PrintDesc(int arr[], int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int max = i; for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) { if (arr[max] < arr[j]) max = j; } cout << arr[max] << ' '; int temp = arr[max]; arr[max] = arr[i]; arr[i] = temp; } cout << endl; }176 : 함수2 - 형성평가2

이 문제는 단순히 생각만 가지고 풀려고하면 헷갈리는 부분이 있습니다.
이런 경우에는 중간 값을 출력하거나 디버그 기능을 사용해서 값을 확인하면서 풀면 쉽게 해결이 가능합니다.
#include <iostream> #include <cmath> using namespace std; void PrintIntCount(float var1, float var2); int main(void) { float var1, var2; cin >> var1 >> var2; PrintIntCount(var1, var2); } void PrintIntCount(float var1, float var2) { int beg = ceil(sqrt((var1 < var2) ? var1 : var2)); int end = floor(sqrt((var1 > var2) ? var1 : var2)); int count = 0; for (int i = beg; i <= end; ++i) count++; cout << count << endl; }177 : 함수2 - 형성평가3

#include <iostream> using namespace std; void PrintAbsSum(int arr[]); int main(void) { int arr[5]; for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) cin >> arr[i]; PrintAbsSum(arr); } void PrintAbsSum(int arr[]) { int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { sum += arr[i] > 0 ? arr[i] : -arr[i]; } cout << sum << endl; }178 : 함수2 - 형성평가4

#include <iostream> using namespace std; int Pow2(int n); int main(void) { int n; cin >> n; cout << Pow2(n) << endl; } int Pow2(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) result *= 2; return result; }179 : 함수2 - 형성평가5

#include <iostream> using namespace std; void Func(float a, float b, float c); int main(void) { float a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; Func(a, b, c); } void Func(float a, float b, float c) { float sumf = a + b + c; float avgf = sumf / 3; int avg = static_cast<int>(avgf + 0.5f); cout << avg << endl; sumf = static_cast<int>(a + 0.5f) + static_cast<int>(b + 0.5f) + static_cast<int>(c + 0.5f); avgf = sumf / 3; avg = static_cast<int>(avgf + 0.5f); cout << avg << endl; }180 : 함수2 - 형성평가6

#include <iostream> #define COUNT 7 using namespace std; void Swap(int& a, int& b); int main(void) { int arr[COUNT]; for (int i = 0; i < COUNT; ++i) cin >> arr[i]; for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < COUNT - 1 - i; ++j) { if (arr[j + 1] < arr[j]) Swap(arr[j + 1], arr[j]); } } for (int i = 0; i < COUNT; ++i) cout << arr[i] << ' '; cout << endl; } void Swap(int& a, int& b) { int temp = a; a = b; b = temp; }181 : 함수2 - 형성평가7

이 문제는 C++ 코드로 처리할 수 없습니다.
float GetCircleSize(float r) { return PI * r * r; }이렇게 함수를 작성하면 결과는 다음과 같이 버림 처리를 해야하는 것으로 나옵니다.

그래서 버림 처리를 하면 결과에 반올림을 해야 하는 것으로 나옵니다.
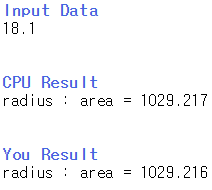
결과적으로 C언어로 처리하면 해결은 가능합니다만 영 결과가 찜찜하네요.
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #define PI 3.141592 void func(double radius) { printf("area = %.3f\n", PI * radius * radius); } int main(void) { double radius; cout << "radius : "; cin >> radius; func(radius); return 0; }위 문제를 문의한 결과 정밀도 문제인 것 같네요. double을 사용하면 해결이 가능합니다.
#include <iostream> #define PI 3.141592 using namespace std; double GetCircleSize(double r); int main(void) { double radius; cout << "radius : "; cin >> radius; cout.setf(ios::fixed); cout.precision(3); cout << "area = " << GetCircleSize(radius) << endl; } double GetCircleSize(double r) { return PI * r * r; }http://www.jungol.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=pbank&sca=10c0
JUNGOL | 문제은행 1 페이지
www.jungol.co.kr